Asphalt Quality Control
For this project, the main objective was to identify a portable and inexpensive solution for checking proper chemical composition of asphalt samples. We inspected the effectiveness of SCiO Molecular Sensor which allows users to train it to identify correct samples using spectrogram. The way it works is that users can scan their materials using the sensor and the smartphone application fetches the data via bluetooth and sends it to cloud server. Users can also modify pre processing methods to find the best model for each material. We made 12 spectrograph models for different grades of asphalts and developed an android application using SCiO's provided API.

Challenges Faced
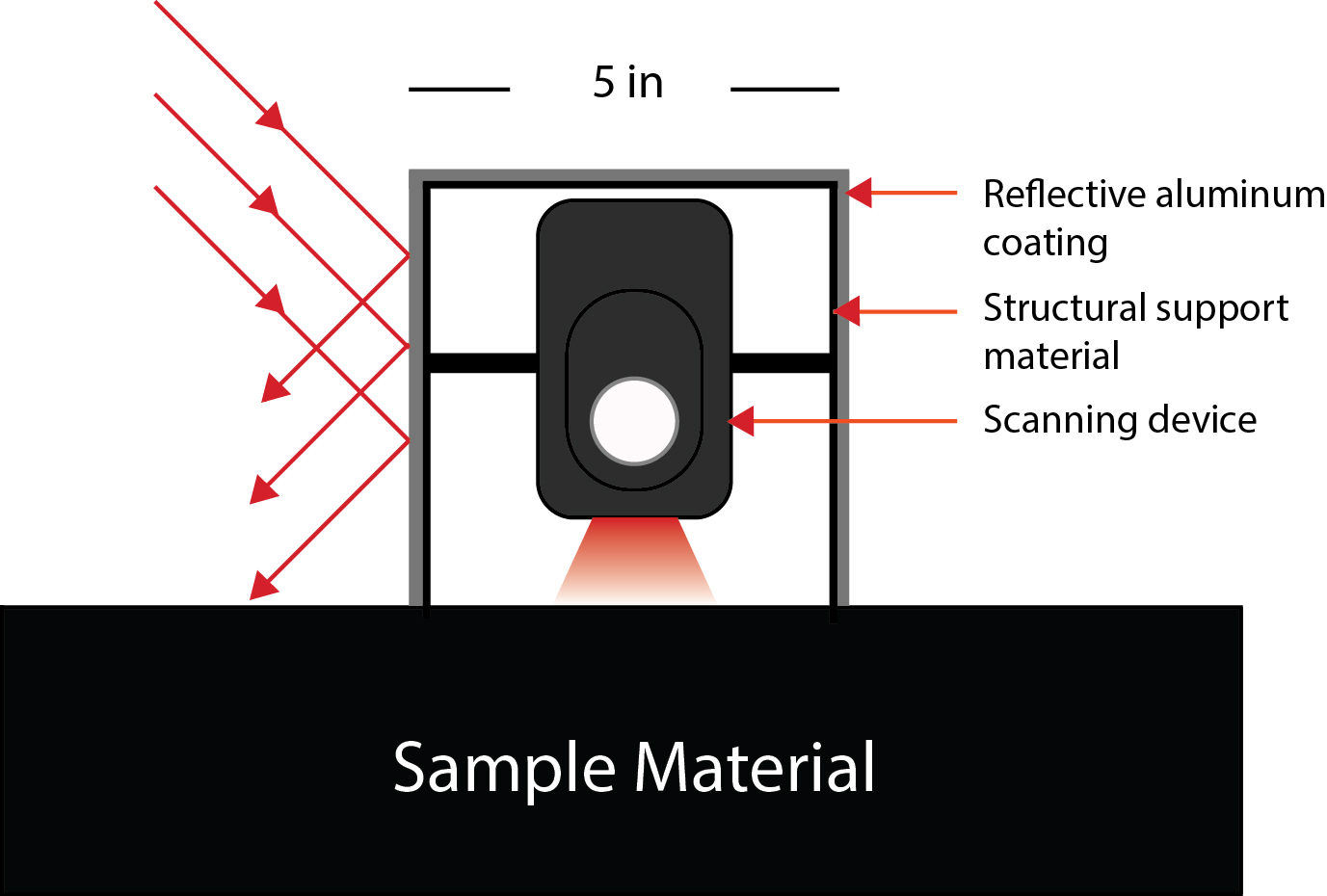
SCiO is a device which uses near-IR spectroscopy. Near-IR ranges from 0.75 to 1.5 microns. But sunlight contains light with every wavelength ranging from 0 microns to 2.5 microns with different intensity levels. So, if we need to block complete range if near IR, we need to use electrically conductive material. Aluminum foil, and other electrically conductive metals such as copper, can reflect and absorb the radio waves and consequently interferes with their transmission. Both radio waves and light waves are electromagnetic waves. And electrically conductive material will block IR. The greater the conductivity, the greater the blocking. Aluminum foil will kill all IR, bot high range and low. Most plastics allow IR to pass through. Glass will bock low frequency IR (red hot), but allow the passage of high frequency (white hot) IR.
Solutions
Reflection by metals is caused by the fact that the outer electrons are very loosely bound to any particular atom. They are, effectively, shared by all the surrounding atoms. This accounts for the high electrical and thermal conductivity of metals. When any electromagnetic wave arrives at a metal surface, the conduction electrons are vibrated by the varying fields and re radiate the energy as a reflected wave. In other words, Electromagnetic radiation falling on the foil causes these electrons to move, and that motion produces new electromagnetic radiation which generates new radiation which destructively interferes with the original incoming radiation. For a flat surface, a mirror (coherent) reflection is produced. This works for light, IR and all radio waves.